초보자를 위한 Linux dpkg 명령 자습서(예제 8개)
이 페이지에서
- Linux dpkg 명령
- Q1. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지를 설치하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q2. dpkg를 사용하여 이미 설치된 패키지를 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q3. 시스템에 설치된 모든 패키지를 나열하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q4. 패키지의 dpkg 목록 내용을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- Q5. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지의 압축을 푸는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q6. 패키지가 설치되었는지 여부를 확인하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q7. dpkg가 설치하는 패키지의 아키텍처를 인쇄하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- Q8. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지를 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?\n
- 결론
Debian 또는 Debian 기반 시스템(예: Ubuntu)을 사용하는 경우 .deb 패키지를 접했을 가능성이 높습니다. 이들은 Debian 패키지이며 Linux 명령줄은 이러한 종류의 패키지를 처리하기 위한 내장 명령/도구를 제공합니다. 이러한 도구 중 하나는 dpkg이며 이 자습서에서 설명합니다.
하지만 그 전에 이 튜토리얼의 모든 예제가 Ubuntu 16.04LTS 시스템에서 테스트되었음을 언급할 가치가 있습니다.
리눅스 dpkg 명령
dpkg 도구는 기본적으로 Debian/Debian 기반 시스템용 패키지 관리자입니다. 구문은 다음과 같습니다.
dpkg ACTIONS
또는
dpkg [options] filename
매뉴얼 페이지에서 설명하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
dpkg is a tool to install, build, remove and manage Debian packages.
The primary and more user-friendly front-end for dpkg is aptitude(1).
dpkg itself is controlled entirely via command line parameters, which
consist of exactly one action and zero or more options. The action-
parameter tells dpkg what to do and options control the behavior of the
action in some way.
dpkg can also be used as a front-end to dpkg-deb(1) and dpkg-query(1).
The list of supported actions can be found later on in the ACTIONS sec?
tion. If any such action is encountered dpkg just runs dpkg-deb or
dpkg-query with the parameters given to it, but no specific options are
currently passed to them, to use any such option the back-ends need to
be called directly.
다음은 dpkg 작동 방식에 대한 좋은 기본 아이디어를 제공하는 몇 가지 Q&A 스타일의 예입니다.
Q1. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지를 설치하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이것은 -i 명령줄 옵션을 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
dpkg -i [package-name]
예를 들어:
dpkg -i google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
다음은 설치 프로세스와 관련된 모든 단계입니다.
1. Extract the control files of the new package.
2. If another version of the same package was installed before
the new installation, execute prerm script of the old package.
3. Run preinst script, if provided by the package.
4. Unpack the new files, and at the same time back up the old
files, so that if something goes wrong, they can be restored.
5. If another version of the same package was installed before
the new installation, execute the postrm script of the old pack?
age. Note that this script is executed after the preinst script
of the new package, because new files are written at the same
time old files are removed.
6. Configure the package. See --configure for detailed informa?
tion about how this is done.
Q2. dpkg를 사용하여 이미 설치된 패키지를 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이것은 -r 명령줄 옵션을 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
dpkg -r [package-name]
예를 들어:
dpkg -r googler_3.3.0-1_all.deb
이 옵션에 대한 매뉴얼 페이지의 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
Removing of a package consists of the following steps:
1. Run prerm script
2. Remove the installed files
3. Run postrm script
Q3. 시스템에 설치된 모든 패키지를 나열하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이를 위해 -l 명령줄 옵션을 사용할 수 있습니다.
dpkg -l
예를 들어, 이 명령줄 옵션이 내 시스템에서 생성된 출력은 다음과 같습니다.
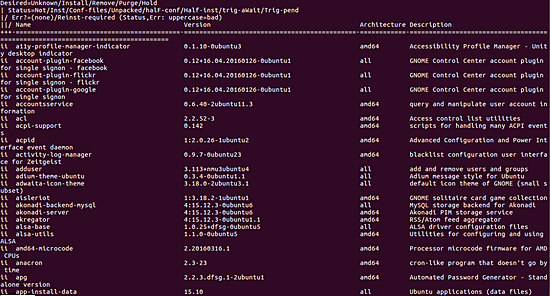
Q4. 패키지의 dpkg 목록 내용을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이는 --contents 플래그를 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
dpkg --contents [package name]
예를 들어:
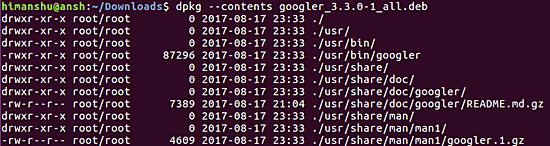
Q5. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지의 압축을 푸는 방법은 무엇입니까?
패키지를 구성하지 않고 압축을 풀고 싶을 때가 있을 수 있습니다. 음, dpkg는 이것에 대한 옵션도 제공합니다: --unpack.
dpkg --unpack [package-name]
나중에 이미 압축을 푼 패키지를 구성하려면 --configure 명령줄 옵션을 사용하면 됩니다.
dpkg --configure [package-name]
다음은 이 옵션에 대한 매뉴얼 페이지의 내용입니다.
Configuring consists of the following steps:
1. Unpack the conffiles, and at the same time back up the old
conffiles, so that they can be restored if something goes wrong.
2. Run postinst script, if provided by the package.
Q6. 패키지가 설치되었는지 여부를 확인하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이를 위해 -s 명령줄 옵션을 사용합니다.
dpkg -s [package-name]
예를 들어:

Q7. dpkg가 설치하는 패키지의 아키텍처를 인쇄하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
이 정보는 --print-architecture 명령줄 옵션을 사용하여 액세스할 수 있습니다.
dpkg --print-architecture
예를 들어 위 명령이 내 시스템에서 생성한 출력은 다음과 같습니다.
amd64
Q8. dpkg를 사용하여 패키지를 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
dpkg 명령을 사용하여 패키지를 제거하는 방법에 대해서는 이미 논의했습니다. conffile을 포함하여 모든 것을 제거하는 프로세스인 패키지를 제거할 수도 있습니다. 이것은 -P 명령줄 옵션을 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
dpkg -P [package-name]
이 옵션에 대한 매뉴얼 페이지의 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
Some configuration files might be unknown to dpkg because
they are created and handled separately through the configura?
tion scripts. In that case, dpkg won't remove them by itself,
but the package's postrm script (which is called by dpkg), has
to take care of their removal during purge. Of course, this only
applies to files in system directories, not configuration files
written to individual users' home directories.
Purging of a package consists of the following steps:
1. Remove the package, if not already removed. See --remove for
detailed information about how this is done.
2. Run postrm script.
결론
dpkg 명령은 다양한 옵션을 제공합니다. 여기서 논의한 내용은 도구를 시작하는 데 도움이 되는 옵션입니다. 연습을 마친 후에는 명령어 매뉴얼 페이지로 이동하여 자세한 내용을 확인하세요.